✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 1997
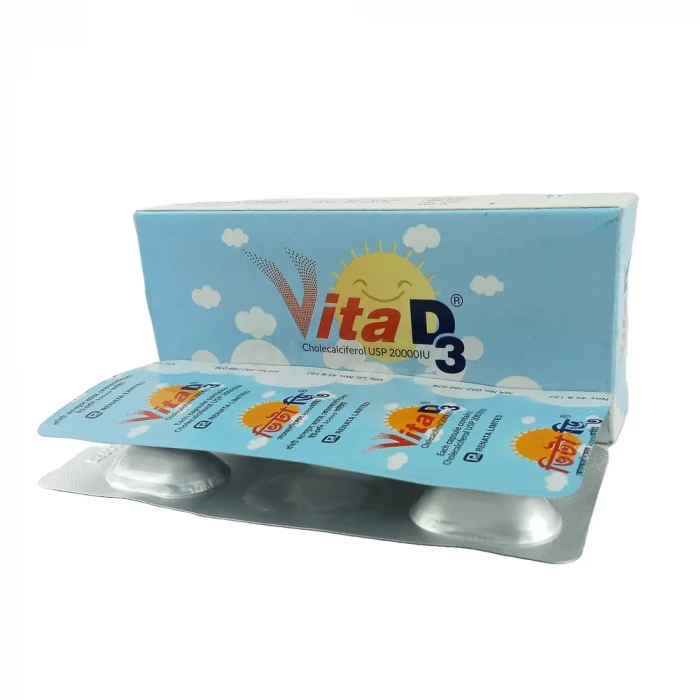
Vita D3 20000IU 5pcs Capsule
Cholecalciferol [Vitamin D3] 20000 IU is used to treat Osteoporosis
- Hypoparathyroidism
- Rickets
- Osteomalacia
- Vitamin D Deficiency
- Pseudohypoparathyroidism
- Familial Hypophosphatemia
Discount
Price: ৳ 98
MRP:
৳
100
2%
Off

100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed

Safe & Secure Payments, Always

Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery

Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed
Safe & Secure Payments, Always
Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery
Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
✅ Description:
Vitamin D3 deficiency can occur in individuals with limited sun exposure or inadequate dietary intake. Vitamin D3 is crucial for the absorption of calcium and phosphate, essential for healthy bones and teeth, and for preventing conditions such as rickets, osteomalacia, and osteoporosis. It is also vital during pregnancy and breastfeeding to prevent pre-eclampsia and support infant growth. Additionally, Vitamin D3 plays a key role in boosting immunity.
✔️ Uses of Vita D3 20000IU
- Nutritional Deficiency
✔️ Side Effects of Vita D3 20000IU
While generally safe, side effects may include:
- Hypercalcemia syndrome or calcium intoxication
- Acute symptoms: anorexia, headache, dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or constipation
✔️ Indication of Vita D3 20000IU
Vitamin D3 is a fat-soluble sterol essential for the regulation of calcium and phosphate homeostasis and bone mineralization. It enhances calcium absorption from the gastrointestinal tract and stimulates bone formation.
✔️ Pharmacology
The active form of Vitamin D3, Calcitriol, binds to Vitamin D receptors (VDRs) in various body tissues. Vitamin D3, being fat-soluble, has a half-life of around 50 days. It is absorbed in the small intestine, transported to the liver, and metabolized to 25-hydroxy Vitamin D3 (Calcidiol). Further hydroxylation occurs in the kidney, forming 1,25-dihydroxy Vitamin D3 (Calcitriol), which facilitates calcium absorption. Non-metabolized Vitamin D3 is stored in fat and muscle tissues and is excreted via feces and urine.
✔️ Dosage & Administration of Vita D3 20000IU
Adult Dose
- Nutritional Deficiency: Oral/IM: 5-10 mcg or 1-2 ml (200-400 IU) daily.
- Osteoporosis Prophylaxis and Treatment (Age >50): 800-1000 IU (20-25 mcg) orally daily with calcium supplements. May also be administered via IM injection.
- Hypoparathyroidism: 50,000-200,000 IU (0.625-5 mg) orally daily with calcium supplements. May also be administered via IM injection.
Child Dose
Nutritional Supplementation:
- 0-12 months: 400 IU (10 mcg) orally daily.
- 1-18 years: 600 IU (15 mcg) orally daily.
- Vitamin D-Resistant Rickets: 12,000-500,000 IU (0.3-12.5 mg) orally daily.
- Familial Hypophosphatemia: 40,000-80,000 IU (1-2 mg) orally daily with phosphate supplements; dosage may be reduced after the growth phase is complete.
✔️ Interaction of Vita D3 20000IU
- Increased Risk of Hypercalcemia: When taken with thiazide diuretics, calcium, or phosphate supplements.
- Antiepileptics: (e.g., carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone) may increase vitamin D requirements.
- Rifampicin & Isoniazid: May reduce vitamin D efficacy.
- Corticosteroids: May counteract the effects of vitamin D.
- Digoxin or Other Cardiac Glycosides: Risk of hypercalcemia.
- Reduced Absorption: When taken with cholestyramine, colestipol, mineral oil, or orlistat.
- Ketoconazole: Interaction may occur.
✔️ Contraindications
Colecalciferol is contraindicated in conditions associated with hypercalcemia and in patients with known hypersensitivity to Colecalciferol or its excipients. It is also contraindicated in cases of vitamin D toxicity.
✔️ Pregnancy & Lactation
Doses up to 4,000 IU are considered safe during pregnancy. The recommended daily intake for pregnant women is 400 IU, though higher doses may be needed for those deficient in Vitamin D3. Pregnant women should follow medical advice specific to their condition.
Vitamin D3 and its metabolites are excreted in breast milk, but no overdosing effects in infants have been observed. When prescribing additional Vitamin D3 to a breastfed child, the mother's dose should be considered.
✔️ Precautions & Warnings
Exercise caution when considering vitamin D supplements in individuals with:
- High blood calcium or phosphorus levels
- Heart problems
- Kidney disease
Vitamin D should be taken with adequate calcium and magnesium. During lactation, vitamin D is distributed into breast milk; use with caution.
✔️ Storage:
Store below 30°C, protected from light and moisture. Keep out of reach of children
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.